How indicators work
Hello everyone, today we are going to look further into the way indicators work. We must say that indicators are weak organic acids or bases.
Let us recall that a weak acid or base does not dissociate completely in solution. We can thus write a dynamic equilibrium that is set up when the indicator molecule is dissolved in water.
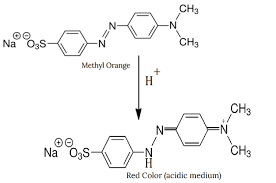
The color changes of solutions that occur in acidic, basic or neutral media when an indicator is added to each stems from the fact that the color of the protonated and deprotonated forms of the indicator are different.
It is safe to say that the degree of dissociation of the indicator depends on the concentration of the hydrogen ion in the medium (which is also the pH) of the solution.
Let us consider the indicator HIn which can have a deprotonated form In-. Then we have that;
HIn > H^+ + In-
It follows that Kin is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the indicator as in;
Kin = [H^+] [In-]/[HIn]
We can rearrange the equation to have that;
Kin/[H^+] = [In-]/[HIn]
Taking the negative logarithm of all the terms in the equation;
-logKin – log[H^+] = -log [In-]/[HIn]
Again;
-logKin = pKin (See our definition of pKa on the page timeline)
– log[H^+] = pH (See our definition of pH on the page timeline)
Thus;
pKin + pH = -log [In-]/[HIn]
pH = pKin + log [In-]/[HIn]
The color changes occur when there is a shift in the equilibrium position and the ratio [In-]/[HIn] changes. When [In-]= [HIn] then pH = pKin. This is when the color of the indicator in a neutral solution is observed(equivalence point or more practically, the end point).
If [In-]>[HIn], the color of the indicator in basic solution is observed. If [In-]<[HIn], the color of the indicator in acidic solution is observed. Tomorrow, we shall look at idea of the pH range of color change in greater detail.
Hope you enjoyed our lesson today?
Follow our page and share!
Do you have assignments, term papers, projects and difficult homework questions? Contact us for help now! We also offer home and remote tutoring services to students at all levels in science subjects.
.png)
.jpeg)
_1.jpeg)
.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment