Introduction to Indicators
Hello fam! Welcome back from the short break. I believe that we are all enjoying the summer holidays. We will now continue from a new topic after we discussed about salts last week.
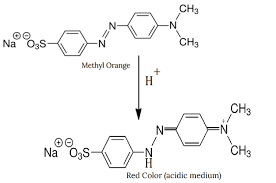
Today, we want to look at the concept of indicators. We need to know that an indicator is a substance that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base.
The idea of the color change is the first thing that you have to bear in mind about the indicators. Many of us have at one time or another titrated an acid against a base or vice versa.
The point at which the acid and base have completely reacted in accordance with the stoichiometry of the reaction equation is called the equivalence point.
Let me give you a typical example; Look at the reaction;
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) -- Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
This reaction would be complete when two moles of sodium hydroxide react with exactly one mole of sulfuric acid. In other words, the amount of titrant added is just enough to neutralize the analyte solution.
How do I know when the amount of titrant added is just enough to neutralize the analyte solution? I have to depend on some kind of reagent that would visually indicate this point.
Any reagent that can visually indicate the point at which the amount of titrant added is just enough to neutralize the analyte solution is called an indicator.
The indicator solution has a different color in acidic, basic and neutral solutions. Hence, an indicator solution is added in drops to an acid or base analyte solution before the titrant is added. The point at which the color of the solution changes during titration is the equivalence point of the solution.
In everyday experiments in the laboratory, we use the endpoint to determine the amount of substance present in an analyte during volumetric analysis. The end point and the equivalence point are not exactly the same. However, we approximate the both to be equal for convenience sake.
The equivalence point is accurately determined from a titration curve and we shall look at that in due course. How exactly does an indicator work? Join us tomorrow to know more!
Hope you enjoyed our lesson today?
Follow our page and share!
Do you have assignments, term papers, projects and difficult homework questions? Contact us for help now! We also offer home and remote tutoring services to students at all levels in science subjects.
.jpeg)
.png)
.png)
_1.jpeg)
.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment